Parameters (inputs)
Please read the section How to inspect the API first. This will explain to you how to inspect the session init response, which is important to understand the following explanations.
Section Inputs and Outputs provides an overview on how to define parameters (inputs) in Grasshopper.
Watch the parameters chapter of our Youtube Video ShapeDiver Geometry Backend API explained!
Definition of parameters on the Geometry Backend API
Consider this simple Grasshopper model which has two parameters Radius and Color, and outputs a colored sphere.
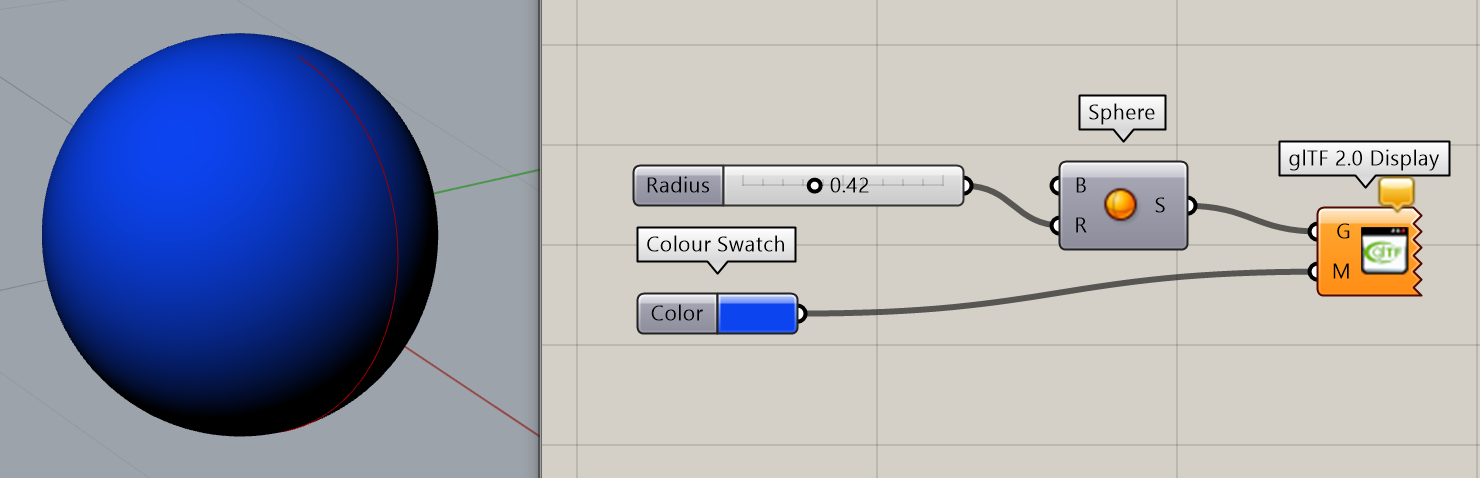
You can view this model here, or upload it yourself.
Inspecting the property parameters of the session init response, we can see both parameters:
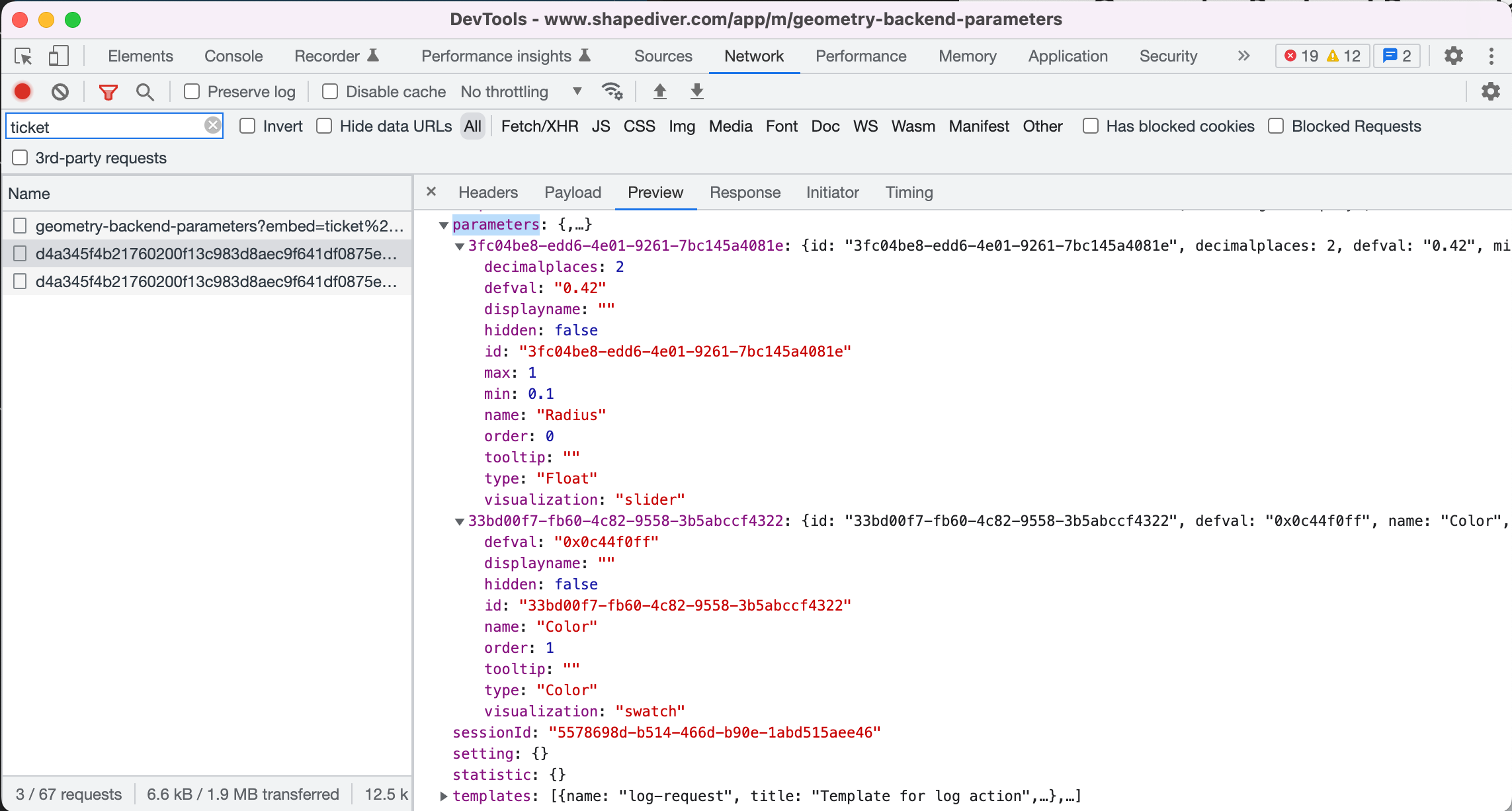
The parameters property contains the definition of the parameters (aka the inputs) that the model exposes. The most important properties of parameters are:
Property | Description |
|---|---|
| The unique id of the parameter, which stays constant each time a model gets uploaded. The |
| Type of the parameter. |
| The default value of the parameter. |
| Name of the parameter as defined by the Grasshopper model. |
| Name of the parameter to display instead of |
You can find the definition of all properties of parameters by searching for “ResponseParameter” in the API documentation. An excerpt:

Parameter values, session state
It is important to understand that the definition of parameters on the Geometry Backend API does not include "current parameter values". There is a default value for each parameter, but no “current value”. In terms of a session on the Geometry Backend API, the parameters are stateless. This stands in contrast to the Session object of the viewer, which actually stores the current parameter values of the model currently shown in the 3D scene.
Parameter values are always represented using strings on the Geometry Backend API. This is a consequence of the caching system and is explained in section TODO.
Section Outputs on the API | Requesting-the-computation-of-outputs explains how parameter values are used to request the computation of outputs.
